Choosing the right dental implant materials is crucial for treatment success. This comprehensive guide compares titanium and ceramic implants to help you make the best decision for your oral health.
1. What Materials Are Implants Made From?
Modern dental implant materials have been carefully developed and tested for safety, biocompatibility, and long-term success. Here’s what today’s implants are made from:
Primary Implant Materials
Titanium implants (most common):
- Pure titanium – Grade 1 and 2 commercially pure titanium
- Titanium alloys – Grade 4 and 5 titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloys
- Surface treatments – Sandblasted, acid-etched, or plasma-sprayed surfaces
- Market share – 95% of all dental implants worldwide
- Track record – Over 50 years of successful clinical use
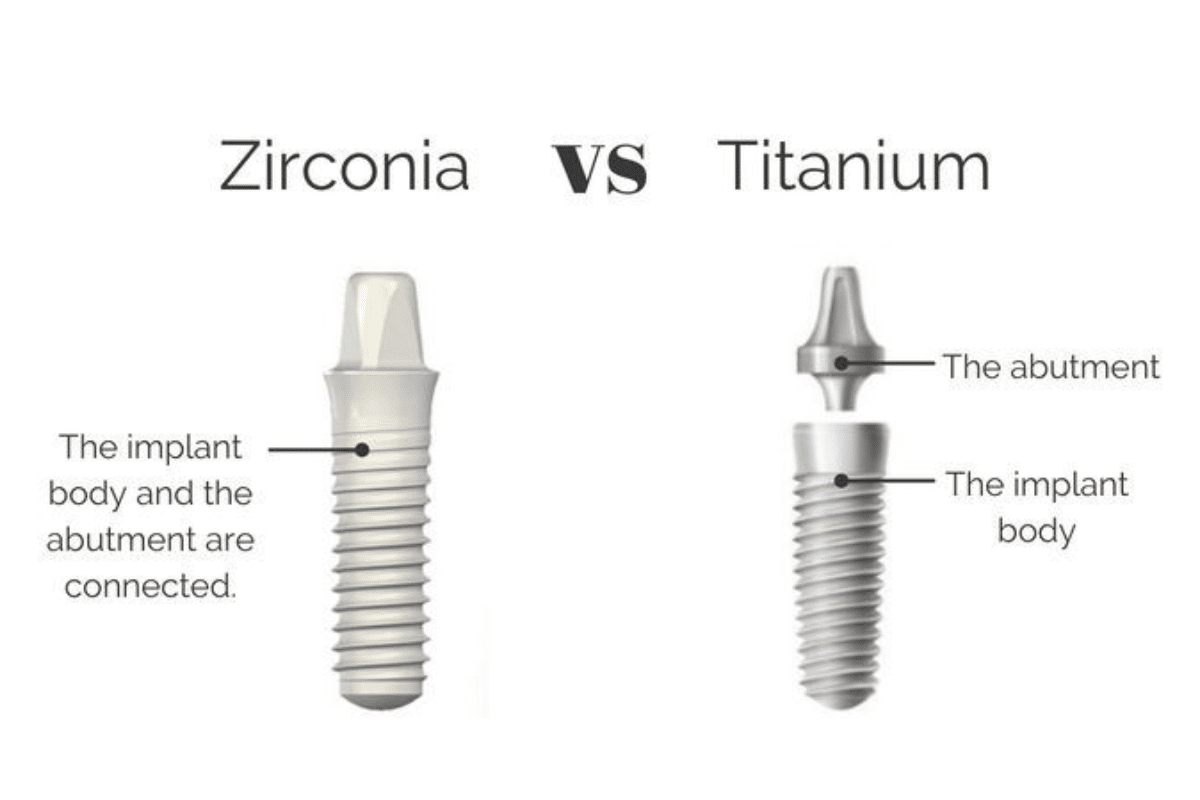
Zirconia (ceramic) implants:
- Yttria-stabilized zirconia – High-strength ceramic material
- One-piece design – Implant and abutment combined
- Metal-free option – No metallic components
- Growing popularity – Increasing demand for metal-free dentistry
- Newer technology – Approximately 20 years of clinical data
Historical Implant Materials
Materials no longer used:
- Stainless steel – Early implant attempts, poor biocompatibility
- Cobalt-chromium – Limited success, replaced by titanium
- Tantalum – Experimental material, not widely adopted
- Gold – Too soft for implant applications
- Aluminum oxide – Early ceramic attempts, inferior to zirconia
Implant Surface Modifications
Titanium surface treatments:
- Machined surface – Smooth titanium finish
- Sandblasted surface – Roughened for better bone attachment
- Acid-etched surface – Microscopic texture for osseointegration
- Plasma-sprayed coating – Hydroxyapatite or titanium coating
- Anodized surface – Electrochemical treatment for enhanced integration
Zirconia surface options:
- Smooth zirconia – Polished ceramic surface
- Roughened zirconia – Sandblasted for bone attachment
- Bioactive coatings – Enhanced integration materials
- Nano-structured surfaces – Advanced surface technology
Biocompatibility Standards
FDA requirements:
- ISO 14801 – Fatigue testing standards
- ISO 10993 – Biological evaluation requirements
- ASTM standards – Material property specifications
- Clinical trials – Extensive human testing required
- Long-term studies – Minimum 5-year follow-up data
Material testing:
- Cytotoxicity – Cell compatibility testing
- Genotoxicity – DNA damage assessment
- Sensitization – Allergic reaction evaluation
- Irritation – Tissue response testing
- Systemic toxicity – Whole-body safety assessment
Manufacturing Quality Control
Titanium implant production:
- Medical-grade materials – USP Class VI certification
- Precision machining – Computer-controlled manufacturing
- Quality assurance – Multiple inspection points
- Sterile packaging – Gamma or electron beam sterilization
- Batch tracking – Complete manufacturing records
Zirconia implant production:
- High-purity zirconia – Medical-grade ceramic powder
- Sintering process – High-temperature forming
- Quality control – Dimensional and strength testing
- Surface finishing – Polishing and treatment
- Sterile packaging – Clean room assembly
Research and Development
Ongoing improvements:
- Surface technology – Enhanced osseointegration
- Material science – Stronger, more durable options
- Bioactive coatings – Faster healing promotion
- Nanostructures – Microscopic surface modifications
- Drug delivery – Antibiotic or growth factor incorporation
At Townsville Dental Clinic, we use only the highest quality dental implant materials with proven track records and FDA approval for optimal patient outcomes.
2. Are Titanium Implants Safe?
Titanium implants are extremely safe with over 50 years of clinical success and millions of successful placements worldwide. Here’s comprehensive safety information:
Titanium Safety Track Record
Clinical success data:
- Success rates – 95-98% long-term success
- Millions placed – Over 100 million titanium implants worldwide
- Decades of use – First successful placement in 1965
- Scientific research – Thousands of published studies
- Global acceptance – Used by dentists in every country
Long-term studies:
- 20+ year follow-up – Excellent durability demonstrated
- Bone health – No negative effects on surrounding bone
- Tissue compatibility – Healthy gum tissue response
- Function maintenance – Normal chewing and speaking
- Patient satisfaction – 95%+ report positive experiences
Biocompatibility of Titanium
Why titanium is safe:
- Bioinert material – Does not react with body tissues
- Osseointegration – Bone grows directly onto titanium surface
- Corrosion resistance – Does not break down in mouth
- Non-toxic – No harmful substances released
- Hypoallergenic – Allergic reactions extremely rare
Body acceptance:
- Immune system tolerance – Body accepts titanium as compatible
- No foreign body reaction – Tissue inflammation minimal
- Stable integration – Permanent bond with bone
- No systemic effects – Remains localized to implant site
- Long-term stability – Properties unchanged over time
Titanium Allergy Concerns
Allergy prevalence:
- Extremely rare – Less than 0.6% of population
- Patch testing – Available if allergy suspected
- Alternative options – Zirconia implants for allergic patients
- Symptoms – Swelling, redness, implant failure if present
- Pre-testing – Can be done before implant placement
Risk factors for titanium sensitivity:
- History of metal allergies – Nickel, cobalt sensitivities
- Jewelry reactions – Previous metal sensitivity
- Occupational exposure – Metalworking industries
- Genetic factors – Family history of allergies
- Multiple metal implants – Other orthopedic implants
FDA Approval and Regulation
Regulatory oversight:
- FDA Class II device – Moderate risk medical device
- 510(k) clearance – Required for all implant systems
- Quality standards – ISO 13485 manufacturing requirements
- Clinical testing – Extensive human trials required
- Post-market surveillance – Ongoing safety monitoring
Material standards:
- ASTM F136 – Titanium Grade 4 specifications
- ASTM F1472 – Titanium Grade 5 alloy standards
- ISO 5832-2 – International titanium standards
- USP Class VI – Biological safety certification
- CE marking – European conformity standards
Titanium in Medical Applications
Widespread medical use:
- Orthopedic implants – Hip, knee, shoulder replacements
- Cardiac devices – Pacemaker components
- Spinal hardware – Rods, screws, plates
- Surgical instruments – Scalpels, forceps, scissors
- Aerospace industry – Aircraft and spacecraft components
Safety across applications:
- Millions of patients – Successful orthopedic implants
- Long-term studies – Decades of safety data
- No increased disease risk – Cancer, autoimmune disorders
- Excellent tolerability – Minimal adverse reactions
- Continuous improvement – Ongoing material refinements
Potential Complications
Rare complications:
- Infection – Related to surgery, not material (1-2%)
- Implant failure – Mechanical or biological (2-5%)
- Nerve damage – Surgical risk, not material-related
- Sinus problems – Upper jaw complications (rare)
- Allergic reaction – Extremely rare (less than 0.6%)
Risk mitigation:
- Proper surgical technique – Sterile procedures
- Patient selection – Healthy candidates
- Quality materials – FDA-approved implants only
- Experienced surgeons – Specialized training
- Follow-up care – Regular monitoring
Research on Titanium Safety
Current studies:
- Ion release – Minimal titanium particle shedding
- Tissue response – Excellent biocompatibility
- Carcinogenicity – No cancer-causing properties
- Reproductive effects – No fertility or pregnancy impacts
- Environmental safety – Sustainable and recyclable
Future developments:
- Surface improvements – Enhanced integration
- Alloy optimization – Stronger, more biocompatible materials
- Coating technology – Bioactive surface treatments
- Manufacturing advances – Better quality control
- Personalized medicine – Patient-specific materials
Special Populations
Pregnancy and nursing:
- Safe during pregnancy – No fetal risks identified
- Breastfeeding – No contraindications
- Timing considerations – Elective procedures can wait
- Emergency treatment – Safe when necessary
Children and adolescents:
- Growth considerations – Wait until facial growth complete
- Trauma cases – Can be placed when appropriate
- Long-term outlook – Excellent durability for young patients
- Special precautions – Careful treatment planning
Elderly patients:
- No age restrictions – Safe for seniors
- Medical conditions – Coordinate with physicians
- Healing considerations – May take longer to integrate
- Quality of life – Significant improvement possible
Townsville Patient Safety
Our safety protocols:
- Material verification – Only FDA-approved titanium implants
- Allergy screening – Pre-treatment assessment
- Quality assurance – Sterile handling procedures
- Patient education – Comprehensive safety information
- Long-term monitoring – Regular follow-up care
For patients in Queensland seeking titanium implants, Townsville Dental Clinic maintains the highest safety standards with proven materials and techniques.
3. What Are Ceramic Implants?
Ceramic implants, primarily made from zirconia, offer a metal-free alternative to titanium implants. Here’s comprehensive information about this growing treatment option:
Zirconia Implant Composition
Material properties:
- Yttria-stabilized zirconia – Y-TZP (Yttria-Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal)
- High-strength ceramic – Flexural strength over 900 MPa
- Biocompatible material – Excellent tissue compatibility
- White color – Natural tooth-like appearance
- Corrosion resistant – No metal ion release
Manufacturing process:
- Ceramic powder – High-purity zirconia particles
- Cold isostatic pressing – Shape formation under pressure
- Sintering – High-temperature consolidation (1500°C)
- Machining – Precision shaping and threading
- Quality control – Dimensional and strength testing
Types of Ceramic Implants
One-piece implants:
- Integrated design – Implant and abutment combined
- Single surgery – No second-stage abutment placement
- Limited adjustability – Fixed abutment angle
- Immediate loading – Often possible with good stability
- Simplified restoration – Direct crown attachment
Two-piece implants:
- Separate components – Implant body and abutment
- Adjustable restoration – Multiple abutment angles
- Traditional protocol – Similar to titanium implant process
- Better aesthetics – Optimal gum line contours
- Newer technology – Limited long-term data
Advantages of Ceramic Implants
Aesthetic benefits:
- Natural color – White like natural tooth roots
- Gum health – Excellent soft tissue response
- No gray shadowing – Prevents dark lines at gum line
- Translucency – Light transmission like natural teeth
- Superior cosmetics – Especially important in front teeth
Biological advantages:
- Metal-free – No metallic components
- Hypoallergenic – No metal sensitivity concerns
- Biocompatible – Excellent tissue acceptance
- Low plaque affinity – Smooth surface resists bacteria
- Non-conductive – No electrical or thermal conduction
Limitations of Ceramic Implants
Mechanical considerations:
- Lower fracture resistance – More brittle than titanium
- Size limitations – Require thicker dimensions for strength
- Limited sizes – Fewer diameter and length options
- Fatigue concerns – Potential for stress fractures
- Repair challenges – Difficult to modify if problems occur
Clinical limitations:
- Less research – Shorter clinical track record
- Fewer options – Limited manufacturer choices
- Higher cost – More expensive than titanium
- Technique sensitive – Requires careful handling
- Limited applications – Not suitable for all cases
Success Rates and Longevity
Clinical outcomes:
- Short-term success – 95-98% at 3-5 years
- Medium-term data – 90-95% at 5-10 years
- Long-term studies – Limited data beyond 10 years
- Survival rates – Comparable to titanium short-term
- Patient satisfaction – High aesthetic satisfaction
Factors affecting success:
- Implant design – One-piece vs two-piece
- Loading protocol – Immediate vs delayed
- Bone quality – Dense bone preferred
- Surgeon experience – Learning curve considerations
- Patient selection – Appropriate case selection
Ideal Candidates for Ceramic Implants
Best candidates:
- Metal allergies – Documented titanium sensitivity
- Aesthetic concerns – Front tooth replacements
- Metal-free preference – Desire for biocompatible materials
- Good bone quality – Dense, healthy jawbone
- Non-smokers – Better healing and integration
Cases to consider carefully:
- Heavy biters – High chewing forces
- Back teeth – Maximum stress areas
- Poor bone quality – Soft or compromised bone
- Immediate loading – Higher stress situations
- Complex restorations – Multiple implants or difficult anatomy
Osseointegration with Zirconia
Bone integration:
- Direct bone contact – Similar to titanium
- Integration timeline – 3-6 months like titanium
- Bone attachment – Mechanical interlocking
- Strength development – Gradual increase over time
- Long-term stability – Excellent bone maintenance
Factors affecting integration:
- Surface texture – Roughened surfaces integrate better
- Implant stability – Initial mechanical fixation important
- Healing environment – Clean, infection-free site
- Loading protocol – Gradual force application
- Patient factors – Age, health, bone quality
Cost Considerations
Ceramic implant costs:
- Material cost – 20-50% more than titanium
- Limited competition – Fewer manufacturers
- Technique demands – May require specialist placement
- Total treatment – $3,500-$6,000 per implant
- Insurance coverage – Similar to titanium implants
Value assessment:
- Aesthetic benefits – Superior appearance
- Biocompatibility – Metal-free option
- Durability questions – Less long-term data
- Patient satisfaction – High aesthetic satisfaction
- Risk vs benefit – Individual case assessment
Current Research
Ongoing studies:
- Long-term outcomes – 15+ year follow-up studies
- Surface modifications – Enhanced integration surfaces
- Strength improvements – Stronger ceramic formulations
- Two-piece systems – Better adjustability options
- Loading protocols – Optimal healing approaches
Future developments:
- Improved materials – Stronger, more durable ceramics
- Better designs – Enhanced clinical performance
- Surface treatments – Bioactive coatings
- Manufacturing advances – Precision and quality improvements
- Cost reduction – Wider availability and competition
Maintenance and Care
Same care as titanium:
- Excellent oral hygiene – Daily brushing and flossing
- Regular cleanings – Professional maintenance
- Avoid hard objects – No ice chewing or bottle opening
- Non-abrasive products – Gentle cleaning materials
- Regular monitoring – Professional examinations
Special considerations:
- Careful handling – More fragile than titanium
- Professional cleaning – Specific instruments may be needed
- Monitoring protocol – Watch for any complications
- Lifestyle factors – Avoid excessive forces
- Long-term follow-up – Regular assessment important
At Townsville Dental Clinic, we offer both titanium and ceramic implant options, helping Queensland patients choose the best material for their specific needs and preferences.
4. Which Implant Material Is Best?
The best implant material depends on your individual needs, medical history, and treatment goals. Here’s how to choose between titanium and ceramic options:
Material Comparison Overview
Titanium advantages:
- Proven track record – 50+ years of successful use
- Highest success rates – 95-98% long-term success
- Extensive research – Thousands of published studies
- Versatile applications – Suitable for all cases
- Cost-effective – Lower material and treatment costs
Ceramic (zirconia) advantages:
- Metal-free option – No metallic components
- Superior aesthetics – Natural white color
- Excellent biocompatibility – Outstanding tissue response
- Hypoallergenic – No metal allergy concerns
- Modern material – Latest dental technology
Decision Factors by Patient Type
Choose titanium implants if you:
- Want proven results – Longest track record of success
- Need maximum strength – Heavy chewing forces
- Have multiple implants – Cost considerations important
- Require back teeth – Maximum durability needed
- Have limited budget – Most cost-effective option
Choose ceramic implants if you:
- Have metal allergies – Documented sensitivities
- Prioritize aesthetics – Front teeth especially
- Want metal-free dentistry – Holistic health approach
- Have thin gums – Risk of metal show-through
- Are younger patient – Decades of wear expected
Clinical Success Comparison
Titanium performance:
- Long-term data – 15-20 year studies available
- Success rates – 95-98% at 10+ years
- Predictable outcomes – Well-understood behavior
- Universal acceptance – Global standard of care
- Extensive experience – Most dentists familiar
Ceramic performance:
- Shorter track record – 10-15 years maximum data
- Promising results – 90-95% success rates
- Improving technology – Rapid developments
- Growing acceptance – Increasing clinical use
- Specialized training – Fewer experienced providers
Aesthetic Considerations
Front teeth (aesthetic zone):
- Ceramic preferred – Natural white color
- Gum health – Excellent soft tissue response
- Light transmission – Natural translucency
- No metal show – Prevents gray shadowing
- Investment value – Superior appearance worth cost
Back teeth (function zone):
- Titanium preferred – Maximum strength needed
- Aesthetics less critical – Not visible when smiling
- Cost effectiveness – Lower treatment cost
- Proven durability – Handles heavy chewing forces
- Wide availability – More size and design options
Medical and Health Factors
Metal allergy considerations:
- Titanium allergy rare – Less than 0.6% prevalence
- Testing available – Patch tests if suspected
- Ceramic alternative – Metal-free option
- Cross-reactivity – Other metal allergies may indicate risk
- Professional assessment – Specialist evaluation recommended
Systemic health factors:
- Autoimmune conditions – May affect material choice
- Medications – Some drugs affect healing
- Diabetes – Both materials suitable with control
- Smoking – Affects both materials equally
- Age considerations – Both suitable for all ages
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Titanium cost-benefit:
- Lower initial cost – $2,500-$4,000 total
- Proven longevity – Excellent long-term value
- Insurance coverage – Standard coverage levels
- Predictable outcomes – Low complication rates
- Wide availability – Competitive pricing
Ceramic cost-benefit:
- Higher initial cost – $3,500-$6,000 total
- Aesthetic value – Superior appearance
- Metal-free benefit – Peace of mind for some patients
- Insurance coverage – Similar to titanium usually
- Long-term value – Uncertain due to limited data
Location-Specific Recommendations
Front teeth recommendations:
- Upper incisors – Ceramic for optimal aesthetics
- Lower incisors – Either material acceptable
- Canines – Consider individual aesthetic needs
- Smile line assessment – Visibility when smiling
- Gum thickness – Thin gums favor ceramic
Back teeth recommendations:
- Premolars – Either material suitable
- Molars – Titanium for maximum strength
- Heavy biters – Titanium preferred
- Grinders – Titanium for durability
- Multiple implants – Titanium for cost considerations
Professional Recommendations
Specialist guidance:
- Individual assessment – Comprehensive evaluation
- Risk-benefit analysis – Weigh all factors
- Patient preferences – Consider personal values
- Long-term planning – Future needs consideration
- Experience level – Provider expertise important
Evidence-based decisions:
- Scientific literature – Current research findings
- Clinical experience – Provider track record
- Patient outcomes – Real-world results
- Technology advances – Latest developments
- Professional consensus – Expert recommendations
Future Considerations
Material developments:
- Titanium improvements – Surface enhancements
- Ceramic advances – Stronger formulations
- Hybrid materials – Combining advantages
- Bioactive coatings – Enhanced integration
- Personalized medicine – Patient-specific materials
Technology trends:
- Digital planning – Better material selection
- Precision manufacturing – Improved quality
- Surface modifications – Enhanced performance
- Biocompatibility testing – Better patient matching
- Cost reductions – Wider accessibility
Making Your Decision
Key questions to ask:
- What are my aesthetic priorities?
- Do I have any metal allergies?
- What is my budget for treatment?
- How important is long-term data?
- What does my dentist recommend?
Decision process:
- Comprehensive consultation – Discuss all options
- Get second opinion – If uncertain
- Review credentials – Provider experience
- Understand warranties – Coverage details
- Plan follow-up care – Long-term maintenance
Townsville Recommendations
Our approach:
- Individual assessment – Comprehensive evaluation
- Material expertise – Experience with both options
- Patient education – Informed decision making
- Quality assurance – Premium materials only
- Long-term support – Ongoing care commitment
Queensland patients benefit from:
- Latest technology – Advanced material options
- Experienced team – Proven results with both materials
- Honest guidance – Unbiased recommendations
- Comprehensive care – Complete treatment planning
- Local expertise – Understanding regional needs
At Townsville Dental Clinic, we help patients choose the optimal implant material based on individual needs, preferences, and clinical factors for the best long-term outcomes.
5. Are There Different Implant Sizes?
Yes, dental implants come in various sizes to accommodate different anatomical needs and clinical situations. Proper sizing is crucial for treatment success and longevity.
Implant Diameter Options
Standard diameters:
- Narrow implants – 3.0-3.5mm diameter
- Regular implants – 3.75-4.2mm diameter
- Wide implants – 4.5-6.0mm diameter
- Mini implants – 1.8-3.0mm diameter
- Platform switching – Different abutment sizes
Clinical applications by diameter:
- 3.0-3.3mm – Lower incisors, limited space
- 3.75-4.2mm – Most common, universal use
- 4.5-5.0mm – Molars, wide extraction sites
- 5.5-6.0mm – Immediate placement, large sockets
- Mini implants – Denture retention, temporary use
Implant Length Variations
Standard lengths:
- Short implants – 6-8mm length
- Standard implants – 10-13mm length
- Long implants – 15-18mm length
- Extra-long implants – 20mm+ length
- Custom lengths – Special order options
Length selection factors:
- Available bone height – Anatomical limitations
- Anatomical structures – Nerves, sinuses, roots
- Bone quality – Soft bone may need longer implants
- Loading requirements – Immediate vs delayed
- Prosthetic needs – Restoration design
Platform Sizes and Designs
Platform diameters:
- Narrow platform – 3.0-3.5mm
- Regular platform – 4.0-4.5mm
- Wide platform – 5.0-6.0mm
- Platform switching – Smaller abutment on larger implant
- Tissue-level design – Platform at gum level
Platform benefits:
- Optimal emergence – Natural crown contours
- Tissue preservation – Maintains gum architecture
- Aesthetic enhancement – Better crown appearance
- Bone maintenance – Reduces crestal bone loss
- Versatile restoration – Multiple abutment options
Size Selection Criteria
Anatomical factors:
- Bone width – Available horizontal space
- Bone height – Vertical space limitations
- Root proximity – Adjacent tooth clearance
- Anatomical structures – Nerves, blood vessels, sinuses
- Tissue thickness – Gum and bone dimensions
Prosthetic considerations:
- Crown size – Natural tooth proportions
- Emergence profile – Crown-to-implant transition
- Occlusal forces – Chewing load distribution
- Aesthetic requirements – Appearance expectations
- Function needs – Specific performance demands
Special Size Applications
Mini implants (1.8-3.0mm):
- Denture stabilization – Removable prosthetic retention
- Narrow spaces – Lower incisors
- Temporary support – Interim solutions
- Limited bone – When standard implants won’t fit
- Cost-effective – Lower cost alternative
Wide implants (5.0-6.0mm):
- Immediate placement – Large extraction sockets
- Molar replacement – High force applications
- Poor bone quality – Increased surface area
- Single-stage surgery – Immediate loading
- Platform switching – Preserve surrounding tissue
Size-Related Success Factors
Diameter considerations:
- Bone-to-implant ratio – Adequate bone around implant
- Stress distribution – Larger diameter spreads forces
- Integration surface – More area for bone attachment
- Loading capacity – Bigger implants handle more force
- Long-term stability – Size affects durability
Length considerations:
- Primary stability – Initial mechanical fixation
- Bone contact area – More length increases surface area
- Force resistance – Longer implants resist lateral forces
- Anatomical limitations – Available bone height
- Success correlation – Minimal length requirements exist
Measurement and Planning
Pre-surgical assessment:
- 3D imaging – CT scans for precise measurements
- Bone density – Quality assessment
- Space analysis – Available dimensions
- Adjacent structures – Critical anatomy mapping
- Treatment planning – Optimal size selection
Surgical guides:
- Computer-planned – Precise size and position
- 3D-printed guides – Accurate implant placement
- Real-time verification – Confirm proper sizing
- Backup plans – Alternative sizes available
- Quality control – Verify placement accuracy
Size Availability by Manufacturer
Major systems offer:
- Multiple diameters – 3.0mm to 6.0mm range
- Various lengths – 6mm to 20mm options
- Platform choices – Different abutment interfaces
- Specialty designs – Unique clinical applications
- Custom options – Special order possibilities
System compatibility:
- Standardized connections – Some systems interchangeable
- Proprietary designs – Manufacturer-specific
- Component matching – Implant-abutment compatibility
- Future serviceability – Long-term part availability
- Quality assurance – Manufacturing standards
Clinical Decision Making
Size selection process:
- Comprehensive planning – 3D analysis and measurement
- Alternative considerations – Multiple size options
- Risk assessment – Anatomical and mechanical factors
- Patient consultation – Discuss options and outcomes
- Final verification – Surgical confirmation
Flexibility during surgery:
- Size adjustment – Change based on surgical findings
- Backup implants – Alternative sizes available
- Real-time decisions – Adapt to actual conditions
- Quality over size – Optimal placement priority
- Safety margins – Conservative approach
Size and Cost Relationships
Pricing factors:
- Standard sizes – Most cost-effective
- Specialty sizes – May cost more
- Custom options – Highest cost
- Volume discounts – Multiple implants
- System selection – Different manufacturers vary
Value considerations:
- Optimal sizing – Better long-term outcomes
- Avoiding complications – Proper size reduces problems
- Aesthetic results – Correct proportions important
- Function optimization – Appropriate force distribution
- Longevity factors – Size affects durability
Regional Considerations
Townsville patient factors:
- Genetic variations – Population-specific anatomy
- Lifestyle factors – Diet and function requirements
- Aesthetic preferences – Cultural considerations
- Treatment accessibility – Available size options
- Follow-up convenience – Local service availability
Queensland dental standards:
- Quality requirements – High material standards
- Professional training – Expertise in sizing decisions
- Technology access – Advanced planning tools
- Patient safety – Conservative sizing approaches
- Outcome tracking – Monitor size-related success
Future Developments
Size innovations:
- Micro implants – Even smaller options
- Tapered designs – Variable diameter
- Short implant advances – Better short implant success
- Custom manufacturing – Patient-specific sizing
- Bioactive surfaces – Enhanced integration
Technology improvements:
- AI planning – Computer-assisted size selection
- Virtual reality – Improved visualization
- Robotic placement – Precise sizing execution
- Material advances – Stronger smaller implants
- Personalized medicine – Individual optimization
At Townsville Dental Clinic, we use advanced 3D planning technology to select optimal implant sizes for each patient’s unique anatomy and treatment needs. Our Queensland team has extensive experience with all implant sizes and systems to ensure the best possible outcomes for every patient.
Choose the Right Implant Materials in Townsville
Selecting the optimal dental implant materials requires expert guidance and careful consideration of your individual needs. Understanding your options helps you make the best decision for long-term success.
Townsville Dental Clinic material expertise:
- Comprehensive experience with titanium and ceramic implants
- Advanced 3D planning for optimal implant sizing
- Quality assurance with only premium materials
- Personalized recommendations based on individual needs
Ready to explore your options?
- Free consultations to discuss material choices
- Complete examination and treatment planning
- Honest guidance on best materials for your case
- Financing options for all implant treatments
Contact Queensland’s implant material specialists at Townsville Dental Clinic for expert guidance on choosing the best dental implant materials for your smile restoration.
Considering dental implant materials in Townsville? Townsville Dental Clinic provides expert guidance on titanium vs ceramic implants with personalized recommendations for optimal outcomes.